- USD 6.49
- View more offers at FS Addon Compare
- Added: October 13, 2022
- Updated: November 11, 2025
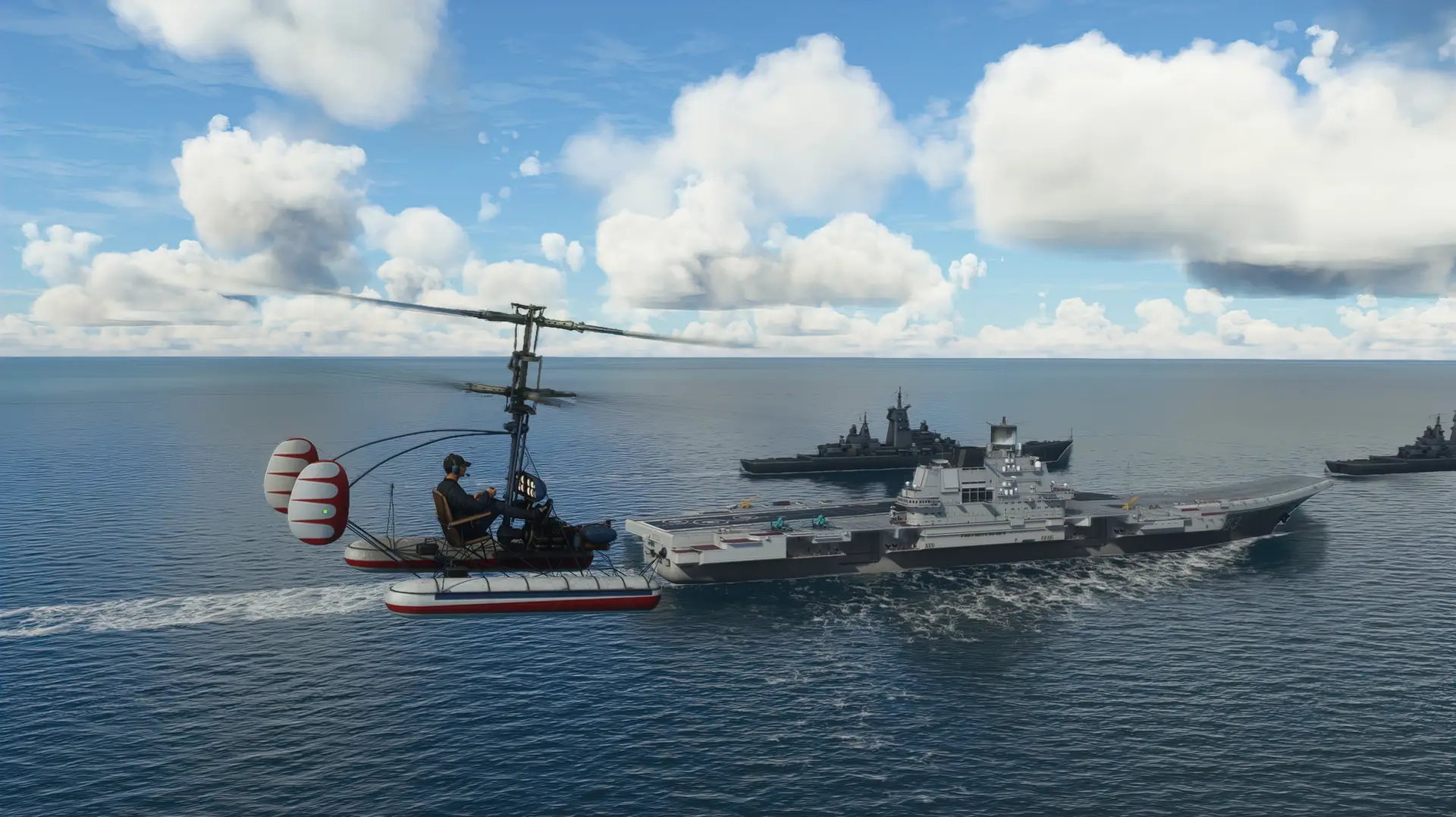
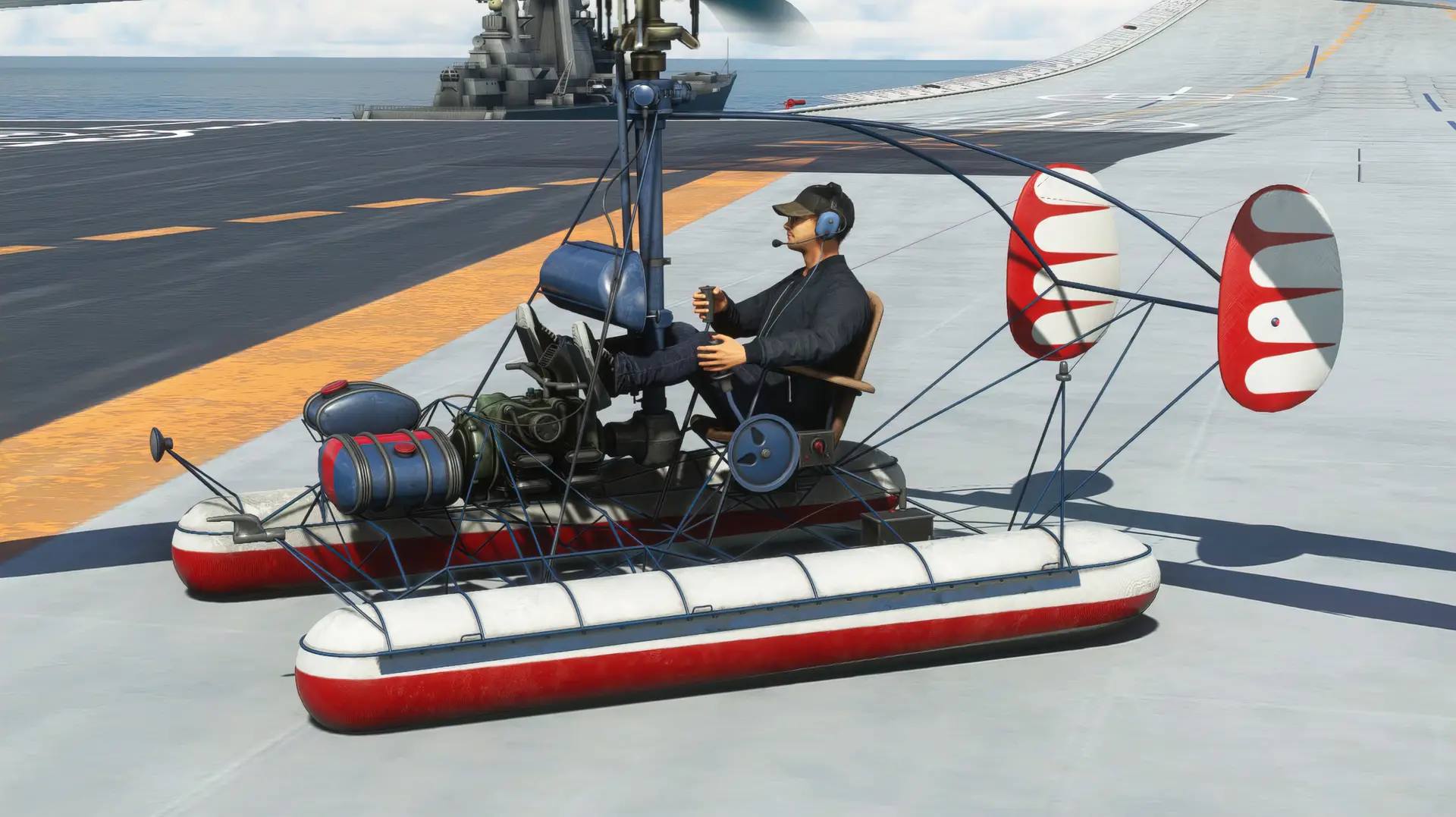
The Kamov Ka-10 (NATO reporting name Hat) is a Soviet single-seat observation helicopter that first flew in 1949. Design and development. It was a development of Nikolay Kamov earlier Ka-8, which had been successful enough to allow Kamov to set up his own OKB (design bureau) in 1948. The Ka-10 made of similar layout to the Ka-8, with an open steel-tube structure carrying an engine, a pilots seat and two three-bladed coaxial rotors. It was larger, however, with a revised transmission and rotor hub design, and a new engine specially designed for the helicopter, the 41 kilowatts (55 hp) Ivchenko AI-4 flat-four.
The Ka-10 made its first flight in September 1949. Three more prototypes followed, which were evaluated by Soviet Naval Aviation. A Ka-10 was displayed at the 1950 Tushino Air Display, and one made the first landing by a Soviet helicopter on the deck of a ship on 7 December 1950.
In 1954, 12 of an improved version, the Ka-10M were built for the Maritime Border Troops. They had a twin tail rather than the single vertical fin of the Ka-10 and modified rotors and control systems.